Weatherization
'Weatherization' is defined as:
The practice of protecting a structure's interior and exterior from the elements. Particularly protecting from precipitation, wind, sunlight, and of modifying a building to reduce energy consumption and optimize energy efficiency.
|
Insulation Envelope
 |
Air Infiltration Envelope
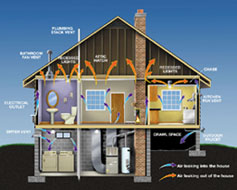 |
Weatherization tips:
- Seal bypasses (cracks, gaps, holes), especially around doors, windows, pipes that penetrate the attic ceiling, pull-downs and attic stair openings, light fixtures, and other areas with high potential for heat loss. Use caulk, foam sealant, weather-stripping, window film, electrical receptacle gaskets, door sweeps, and other items to reduce air infiltration.
- Install insulation in walls, floors, ceilings, and around ducts and pipes, and near the foundation and sill.
- Add an insulation blanket to the hot water heater and consider lower the temperature on your heater to 120 and 125 degrees.
- Seal duct work by ensuring that all ductwork is sealed at joints and intersections with duct sealer, silicone caulk, an/or foil-backed tape (not duct tape)
- Change furnace filters every month and have all heating and cooling equipment service by a professional annually.
- Use a programmable thermostat. In the winter set the thermostat between 65 and 70 degrees. At bedtime and when away from home for several hours set the thermostat back.
- Use solar heating on sunny days. Open drapes/curtains on south-facing windows when it is sunny outside. At night close the drapes to retain the heat and keeps drapes closed on windows that receive no direct sunlight.

